Everything AI can deliver comes from the foundation of the models used.
The evolution of such models has driven the need for fine-tuning, which is an essential step when creating AI systems. It ensures that the models can be applied to specific needs.
However, all fine-tuning isn't the same, and differences emerge when comparing large language models (LLM) like OpenAI's GPT-4 to Google T5. So, what does fine-tuning look like in closed-weight (GPT-4o) and open-weight (T5) models?
In this article, you'll learn the differences between fine-tuning GPT-4 using data provided in formats such as JSONL and fine-tuning a model like T5 using more traditional, fully annotated data.
Understanding Fine-Tuning
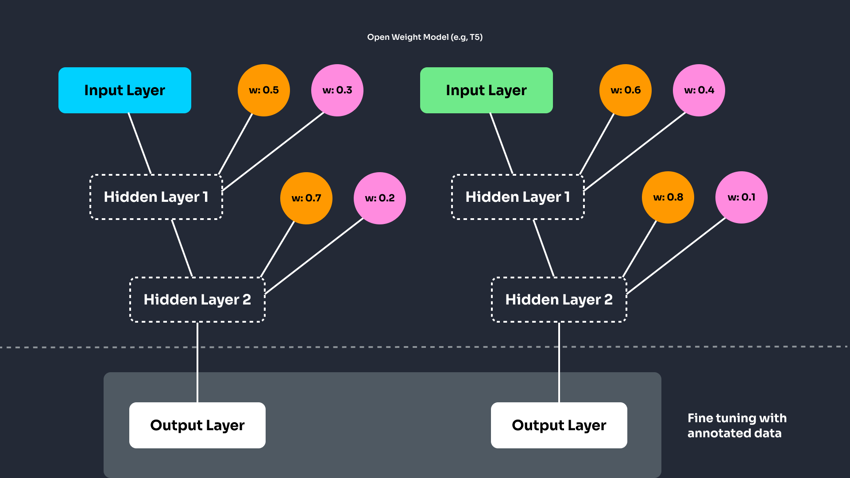
What is fine-tuning of AI models? It's a process that adjusts pre-trained models to accomplish more domain-specific tasks. GPT-4 and T5 both have fine-tuning capabilities, but the depth and control over the model differ significantly.
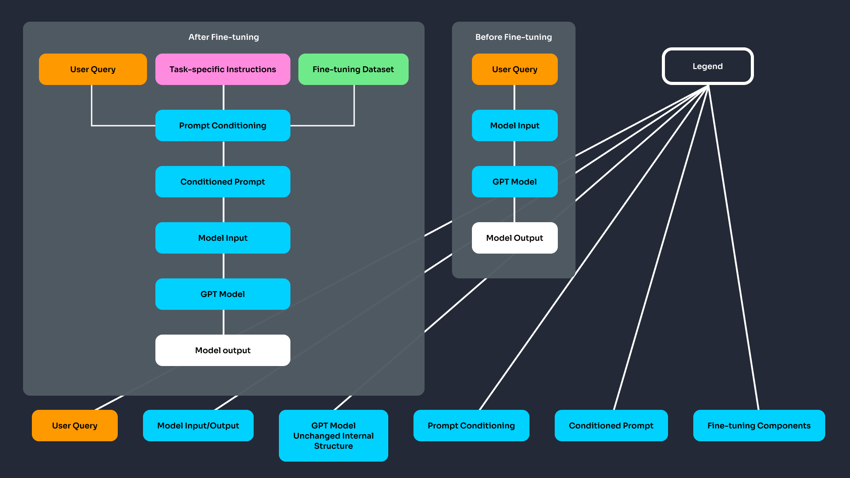
Closed-Weight Models (e.g., GPT-4): These models have weights that are not publicly accessible. Instead of modifying the model's internal structure during fine-tuning, you adjust how the model behaves by providing examples in a format like JSONL. This type of fine-tuning indirectly influences responses but doesn't alter the core model weights.